Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
UV Laser vs Fibre Laser Engraver: What's the Difference?
-
Tags:
- Laser Engraving , Laser Etching , Electric Vehicle
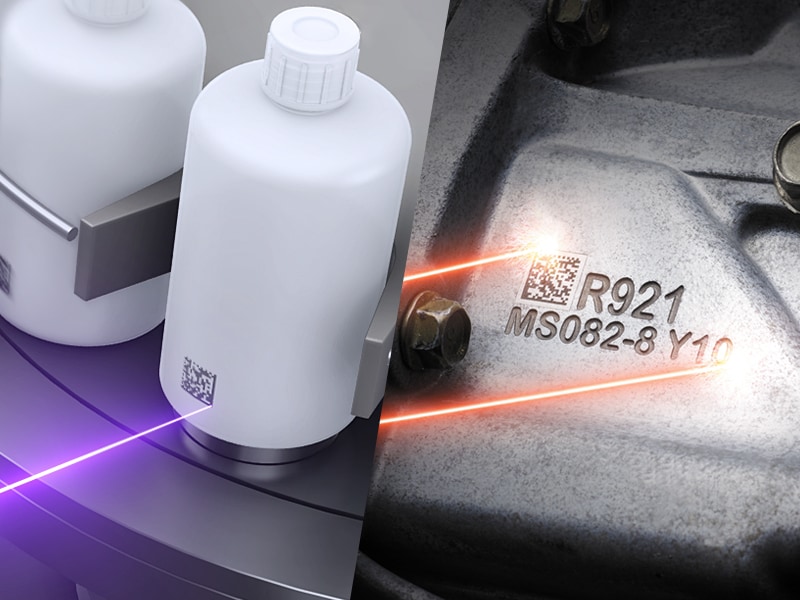

In the debate of using UV lasers vs fibre lasers for engraving, each technology has a purpose in manufacturing. In the following, we will explore both for a better understanding of how they work, their unique benefits, how and where the technology can be applied, and, ultimately, their full potential.
Definition of UV Laser
A UV laser is a laser that uses ultraviolet light to mark materials.
First, a 1064 nm laser is converted into a 355 nm laser through two crystals. Then, the 355 nm beam breaks down bonds directly using a photolytic degradation process. This process is known as “cold marking” because it does not burn surface areas and uses minimal heat stress.
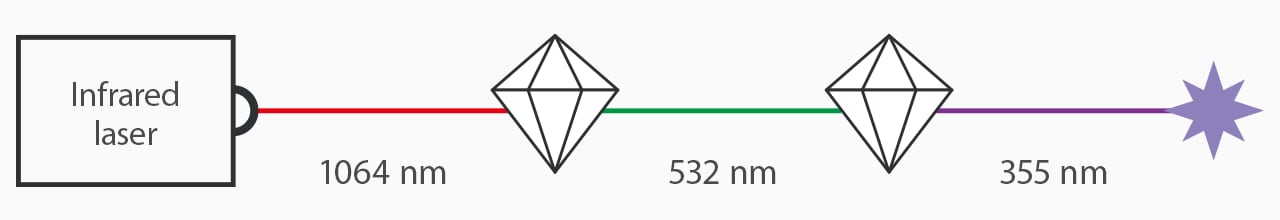
Definition of Fibre Laser
A fibre laser is an infrared laser with a wavelength of 1090 nm. The fibre laser uses heat to cut, engrave, mark, etch, and remove burr. Fibre lasers work great with metals and can be a more affordable option. Widely used for deep engravings and many other production processes, fibre lasers are a go-to choice for many manufacturers.
Even with its efficacy as a laser engraver for metal, this laser design is not perfect for every engraving situation. That is why getting the full scope on fibre laser vs UV laser specifics is crucial so you know how and where to adapt them. KEYENCE’s fibre laser marking machine is the 3-Axis Fibre Laser MD-F Series.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!
Benefits of UV Laser
Damage-Free Marks
UV lasers break down bonds directly, so minimal heat stress is used when marking. Because of this, no residue of burrs or yellow tinting is left over on the marked materials.
The high-energy photons in UV lasers allow for photolytic degradation processing that breaks the bonds between molecules directly. This allows for marking and processing without heat being applied to surfaces, thus minimising damage.
Thermal Processing
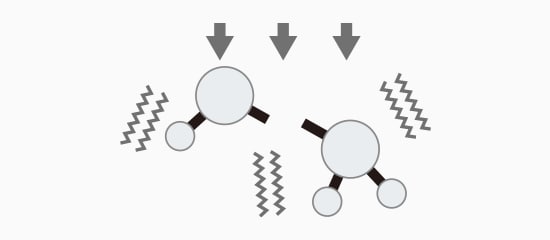
Bonds are destroyed using heat to vibrate the molecules.
Photolytic Degradation Processing
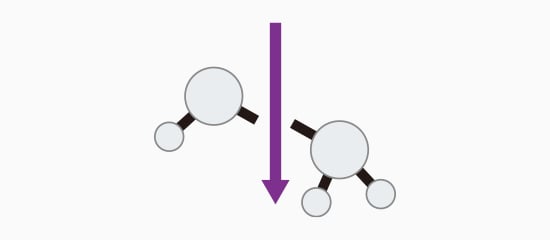
Bonds are broken with light, resulting in less heat.
Easy Marking on Sensitive Materials
Since UV lasers do not rely on heat marking and use absorption, these lasers can mark materials that are heat sensitive and may be damaged by fibre lasers.
Heat-sensitive materials that a UV laser can mark are:
Marking Silver-Plated Surface

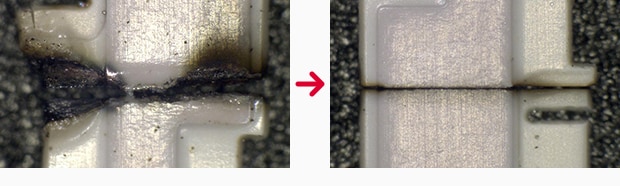
Cutting PCB
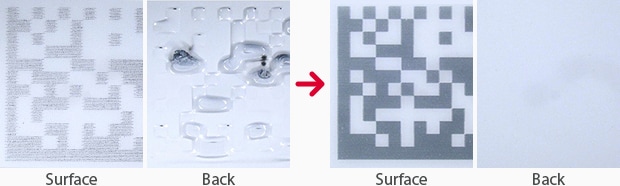
Marking Transfusion Bag Film
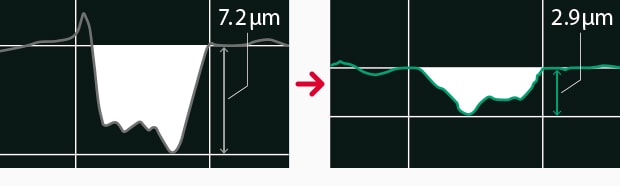
Marking IC Package
Advantages of UV Laser Engraver
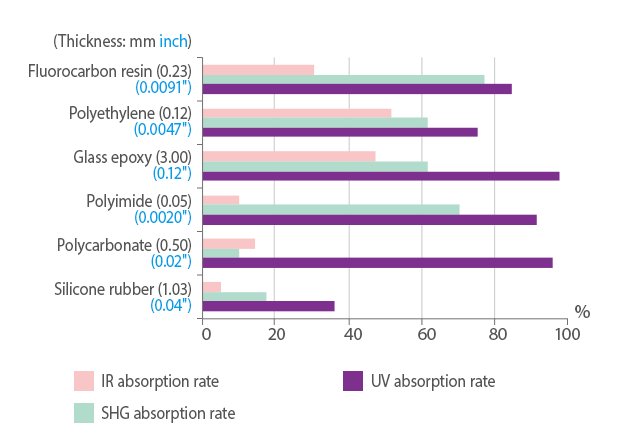
Absorption rates for various resin materials
* The values are for reference only and do not account for surface reflectivity
High Absorption Rate
A UV laser has a 355 nm laser with an incredibly high absorption rate. This means that even with materials that have high melting points, like glass or metal, the UV laser can still mark them without using high power. Additionally, since the absorption rate is so high, the laser does not damage the material.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
Benefits of Fibre Laser
Increased Efficiency with Output
Fibre lasers are known for their high output making for quicker production times. The MD-F Series has two choices of outputs, 30 W and 50 W. With these outputs, the fibre laser can mark, cut, engrave, and anneal materials fast.
High Contrast Metal Marking
For metals like iron that are not highly reflective, the fibre laser can create high contrast marks. Other lasers that have high absorption rates cannot achieve the same effect quickly.
Advantages of Fibre Laser
Scratch Control
Fibre lasers are a good choice for cutting materials because of their high output. The 3-Axis Fibre Laser MD-F Series has scratch control, which allows for clean cuts. The cutting process moves the fibre laser beam back and forth across a short distance. Since the fibre laser beam moves across a short distance, the energy is focused. This results in speedy processing time and clean cuts.
Wobble Control
The MD-F fibre laser achieves high-quality annealing with wobble control. The Wobble control makes the laser move in a circular pattern rather than overlapping single lines. The circular pattern ensures thick characters and concentrated energy.
Deep Engraving Control
The high output of 50 W not only marks fast, but it can engrave deeply. The output's high heat digs deep into materials. With the deep engraving control of the MD-F, the focal distance varies for each laser pass. Because of this, the maximum energy density is achieved throughout the marking.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Differences Between UV and Fibre Lasers
Type of Laser
From a foundational standpoint, a UV laser vs a fibre laser differ greatly. UV lasers use ultraviolet light, while fibre lasers use an infrared light. Additionally, the UV laser is 355 nm while the fibre laser is 1090. Since they have different types of light, each laser has a separate process of marking. Fibre lasers use high heat with high output to mark materials, while UV lasers use absorption to break down bonds.
UV Laser Applications vs Fibre Laser Applications
A UV laser does not rely on heat for marking, so it can mark heat-sensitive materials without damage. On the other hand, fibre lasers do use heat, so they do not have the capability of marking on heat-sensitive materials without damage. However, fibre lasers may be better for certain metals like iron because of the high output creating high contrast.
Speed
When it comes to speed, choosing a UV laser vs a fibre laser depends on the material that you are looking to mark or process. The fibre laser has an output of 50 W, whereas the UV laser has an output of 3 W. Typically this means that the fibre laser would be faster when it comes to marking, cutting, or engraving. However, there are materials, like plastics, that the higher absorption of the UV allows it to mark or engrave faster than the fibre, regardless of the wattage difference.
UV Laser vs Fibre Laser Engraver in Manufacturing
Looking at this technology from a bird’s eye view involves more than the main difference between UV and fibre lasers. Nevertheless, it can’t be ignored that this is one of the core areas of debate surrounding UV laser vs fibre laser comparisons.
As a manufacturer, choosing between the two considers specific nuances of your specific operation. While some businesses may benefit more from UV, others may only need the output and quality that fibre laser engraving offers. Both designs are more than enough in their own right, but providing additional points side by side can help you align the right equipment for your production needs.
For example, some organisations prefer the low heat output of UV laser engravers, as this makes them a great choice for more sensitive materials. The differences between UV and fibre lasers can be seen in the final quality.
While each is more than satisfactory, UV lasers are proven to create smaller spot sizes than fibre lasers. This makes for a more seamless look on non-metal materials.
Potential Innovations and Trends Shaping the Future of UV vs Fibre Laser Engravers
There are many known current applications for fibre and UV laser marking and engraving, but what does this mean for the technology's future?
Here are a few popular innovations and trends with UV and fibre lasers:
- More in-depth integrations with AI and machine learning.
- Better energy efficiency and sustainability practices.
- Laser source technology is bound to improve with time.
- It will eventually become even more cost-effective.
- More applications with eco-conscious manufacturing and recycling efforts.
The list of applications, use cases, and benefits of these tools is ever-growing. We’re living in a technological era full of innovation, which will only make the laser engraving process all the more relevant. If your organisation is looking to make your way into the territory of deep laser engraving, you want to work with the experts on the matter.
KEYENCE’s Comprehensive Range of UV and Fibre Laser Engravers
KEYENCE has decades of experience with laser marking equipment, including UV and fibre laser engravers. Whether you’re focused on laser etching vs engraving or stuck deciding on the type of laser, you can trust we have the quality and variety you need. Here are a few of our most popular engraving machines:
Most consumers won’t settle for less, which means manufacturers will need to keep up with quality standards found in the most recent technology. Traditional methods of laser marking food packaging, car parts, and many other common items are still very relevant.
Conclusion
UV lasers and fibre lasers each have specifications that make them optimal for certain production projects. If your project includes marking heat-sensitive materials or marking on small objects, choosing a UV laser is best. However, if you are looking for a high-speed laser that can achieve clean cuts, engraving, or annealing on metal, you may want to choose a fibre laser.
Whichever you choose, UV laser vs fibre laser, KEYENCE is here to help. At KEYENCE, we have a knowledgeable team that will help you throughout your selection process to operations with on-site operating instructions, along with industry-leading after-sales support.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us