Coaxial Illumination
Optical Illumination Technique - Coaxial Lighting
Viewing highly-reflective objects with flat surfaces, such as ICs and cross-sectioned samples, is typically difficult to accomplish using ring illumination. When light hits the surface, most of it will reflect away from the lens and result in a dark image. Instead, coaxial (brightfield) illumination is used to view these targets and produce a bright image. Generally, this type of lighting makes use of a half-mirror to match the optical axes of the illumination and lens.
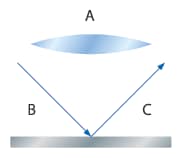
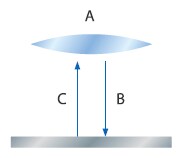
- A
- Lens
- B
- Illumination
- C
- Reflected light
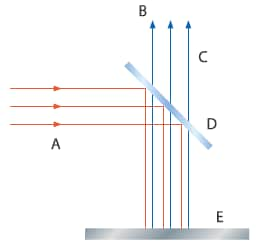
- A
- Illumination
- B
- Lens & CCD
- C
- Specular reflection light
- D
- Half mirror (A half mirror reflects half of the light and transmits the rest)
- E
- Mirrored surface